The automotive repair industry is a massive sector in the United States, with approximately 290,000 auto repair shops generating a staggering $188.1 billion market size as of 2024. For entrepreneurs and investors, a crucial question arises: is owning an auto repair shop profitable? Understanding the financial realities of this industry is vital before taking the plunge.
This article delves into a comprehensive analysis of the profitability of auto repair shops, drawing insights from financial data of over 3,300 real auto repair businesses across the United States. Utilizing publicly available 2023 data from major franchises like Carstar, Fix Auto USA, and Car-X, we aim to provide a clear picture of the revenues, startup costs, and profit margins prevalent in the auto repair sector.
Whether you are contemplating opening your own auto repair business or simply seeking to grasp the financial workings of this industry, this guide offers a detailed exploration of the key elements that influence profitability and return on investment. We will address critical questions such as:
- What is the average revenue for an auto repair shop?
- What are the typical startup costs associated with launching an auto repair shop?
- How profitable can an auto repair shop realistically be?
Decoding Auto Repair Shop Revenues: How Much Can You Earn?
Data analysis from nearly 2,800 auto repair businesses reveals an impressive average annual revenue of $1,226,000. However, it’s crucial to recognize that revenue figures can fluctuate significantly based on factors like geographical location, the range of services offered, brand recognition, and the scale of operations. To provide a more granular perspective, let’s examine the median revenues across different franchises:
| Franchise | Number of Businesses | Median Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| Tire Pros | 623 | n.a. |
| Carstar | 430 | $2,265,000 |
| Fix Auto USA | 178 | $2,391,000 |
| Car-X | 145 | $778,000 |
| Merlin Complete Auto Care | 24 | $1,150,000 |
| Tuffy Tire and Auto Service | 163 | $1,344,000 |
| Abra Auto Body & Glass | 57 | n.a. |
| Honest-1 Auto Care | 64 | $1,149,000 |
| Maaco | 398 | $1,281,000 |
| Meineke Car Care Centers | 705 | $897,000 |
| Rad Air Complete Car Care | 10 | $1,102,000 |
| Weighted Average Revenue | 2,797 | $1,225,778 |

*n.a. indicates non-available data due to franchisor disclosure policies.
This table underscores the revenue potential while highlighting the variability across different franchise models. Factors contributing to revenue differences include brand strength, service specialization (e.g., bodywork vs. general repair), and operational strategies.
Startup Costs: What Investment is Required to Open Shop?
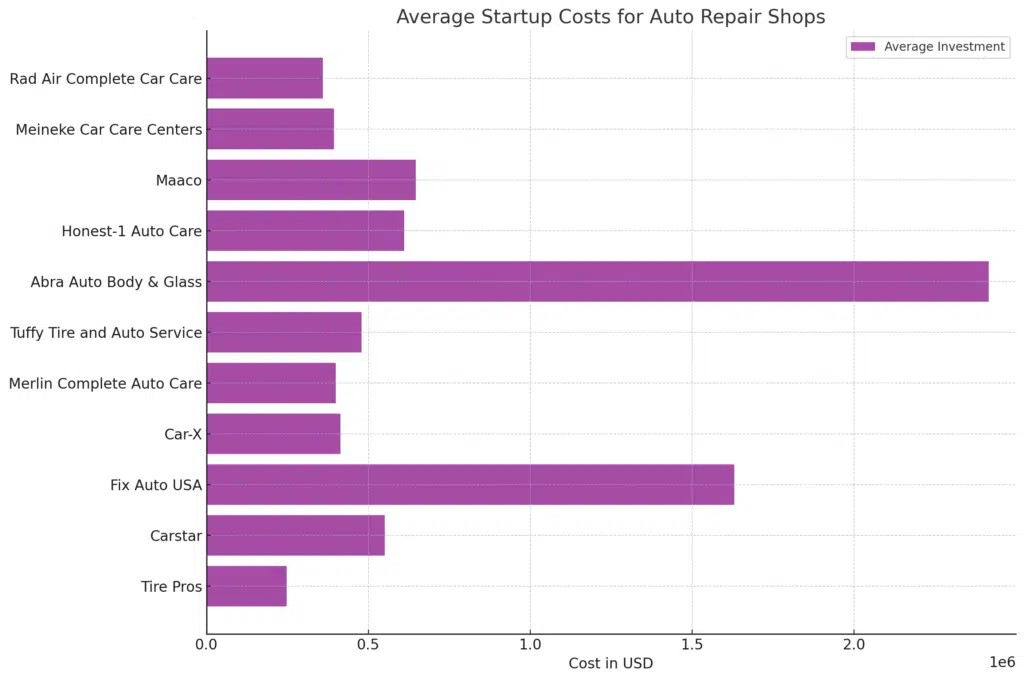
Entering the auto repair business necessitates a significant initial investment. Startup costs can range broadly from $235,000 to $1,348,000. This substantial range reflects the diverse scales of operation, location choices, and franchise affiliations. Let’s break down the investment spectrum based on franchise data:
| Franchise | Low Investment | High Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Tire Pros | $12,000 | $483,000 |
| Carstar | $298,000 | $804,000 |
| Fix Auto USA | $170,000 | $3,090,000 |
| Car-X | $315,000 | $512,000 |
| Merlin Complete Auto Care | $265,000 | $534,000 |
| Tuffy Tire and Auto Service | $229,000 | $729,000 |
| Abra Auto Body & Glass | $264,000 | $4,569,000 |
| Honest-1 Auto Care | $223,000 | $998,000 |
| Maaco | $276,000 | $1,016,000 |
| Meineke Car Care Centers | $227,000 | $562,000 |
| Rad Air Complete Car Care | $146,000 | $573,000 |
| Average Investment | $235,000 | $1,348,000 |
For a more detailed understanding, consider the typical startup costs for a medium-sized auto repair shop, estimated between $200,000 and $500,000:
Breakdown of Startup Costs for a Medium-Sized Auto Repair Shop
- Equipment and Fixtures: Essential repair tools, diagnostic equipment, lifts, and shop furnishings. ($131,000 – $193,000)
- Inventory: Initial stock of common replacement parts, fluids, and supplies. ($5,000 – $24,000)
- Leasehold Improvements: Modifications to the leased space to meet operational needs. ($8,000 – $64,000)
- Training Expenses: Costs for onboarding and training technicians and staff. ($3,000 – $5,000)
- Pre-Opening Expenses: Utility deposits, licenses, permits, and initial setup fees. ($10,000 – $20,000)
- Grand Opening Advertising: Marketing and promotional activities for the launch. ($7,500)
- Signage: Interior and exterior business signage. ($20,000 – $100,000)
- Business Licenses and Permits: Legal and regulatory compliance costs. ($500)
- Real Estate Costs: Initial rent or lease payments. ($0 – $30,000)
- Working Capital (3 months): Funds to cover operational expenses during the initial months. ($10,000 – $50,000)
- Insurance (3 months): Initial insurance premiums for liability and property coverage. ($4,000 – $5,000)
These figures provide a comprehensive overview of the significant upfront investment required to establish a fully functional auto repair shop. Careful planning and financial forecasting are crucial to manage these startup costs effectively.
Profitability Unveiled: How Much Can Auto Repair Shops Actually Make?
Despite the considerable startup investment, auto repair shops can be quite profitable. On average, these businesses report a healthy 26% operating profit margin. This metric represents the profit generated from core operations before accounting for taxes and interest, indicating the inherent profitability of the business model.
Let’s examine the profitability metrics across various auto repair franchises:
Profitability Benchmarks Across Auto Repair Franchises
| Franchise | COGS % | Gross Profit % | Labor Costs % | Operating Profit % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car-X | 35.2% | 64.8% | 30.3% | 19.9% |
| Merlin Complete Auto Care | 28.1% | 71.9% | 16.1% | 38.6% |
| Tuffy Tire and Auto Service | 30.8% | 69.2% | 28.2% | 26.3% |
| Meineke Car Care Centers | 26.3% | 73.7% | 19.2% | 24.2% |
| Rad Air Complete Car Care | 25.3% | 74.7% | 24.7% | 21.0% |
| Average | 29.14% | 70.86% | 23.7% | 26.0% |
These figures reveal that while Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) and labor costs are significant expenses, auto repair shops maintain strong gross profit margins, ultimately translating to a respectable average operating profit. Franchises like Merlin Complete Auto Care demonstrate particularly high operating profit margins, suggesting potential for even greater profitability within the industry.
Operational Costs: Understanding the Expenses of Running an Auto Repair Shop
To fully appreciate the profitability of auto repair shops, it’s essential to understand the ongoing operational costs. These expenses typically include:
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Direct costs of parts and materials used in repairs. (Example: 25-35% of revenue)
- Labor Costs: Technician and staff wages and benefits. (Example: 16-30% of revenue)
- Rent and Utilities: Facility lease payments and utility expenses. (Typically 5-10% of revenue)
- Marketing and Advertising: Promotional and advertising expenses. (Approximately 1-5% of revenue)
- Insurance: Liability, property, and worker’s compensation insurance. (Approximately 2-4% of revenue)
- Supplies and Equipment Maintenance: Tool and equipment upkeep and consumable supplies. (Approximately 2-5% of revenue)
- Administrative Expenses: Office supplies, accounting, and general administration. (Approximately 5-10% of revenue)
- Training and Development: Staff training and professional development. (Approximately 1-3% of revenue)
- Miscellaneous Expenses: Uncategorized operational costs like uniforms and software. (Approximately 1-3% of revenue)
Managing these operational costs effectively is crucial for maximizing profitability. Efficient inventory management, optimized labor scheduling, and strategic marketing initiatives all contribute to a healthier bottom line.
Real-World Example: Maaco Auto Repair Profit & Loss
To illustrate the practical financial performance of an auto repair business, consider the example of Maaco, a large franchise with 398 locations in 2024. Maaco shops, with an average yearly revenue of $1,340,000, achieve a notable 16.8% operating profit per month.
This real-world example demonstrates the potential for substantial revenue and profitability within the auto repair industry, even with varying franchise models.
Conclusion: Is Owning an Auto Repair Shop a Profitable Venture?
Based on the data and analysis, owning an auto repair shop can indeed be a profitable venture. The industry boasts significant market size, substantial average revenues, and healthy operating profit margins. While startup costs are considerable, the potential for return on investment is attractive.
However, success in the auto repair industry is not guaranteed. Profitability hinges on factors like effective cost management, strategic location selection, skilled labor, and robust customer service. Thorough market research, meticulous financial planning, and a commitment to operational excellence are essential for anyone seeking to capitalize on the profitable opportunities within the auto repair sector.
For those seeking a deeper dive into financial planning for an auto repair business, resources like the Auto Repair Financial Model Template can provide valuable tools and insights. By understanding the financial dynamics and implementing sound business practices, entrepreneurs can position themselves for success in this robust and essential industry.
