The automotive repair industry is a massive sector in the United States, with approximately 290,000 auto repair shops contributing to a staggering $188.1 billion market. If you’re considering entering this lucrative field, or simply curious about the financial health of this industry, a crucial question arises: just how much money do auto repair shops actually make? Understanding the earning potential, the initial investment, and the operational costs is vital for anyone looking to navigate or invest in the car repair business.
This in-depth analysis delves into the financial performance of over 3,300 real auto repair businesses across the United States. By examining publicly available data from 2023, encompassing a wide range of franchises including Carstar, Fix Auto USA, and Car-X, we aim to provide you with a clear and data-backed answer to the question: “how much money do auto repair shops make?”. Whether you are contemplating launching your own auto repair venture or seeking a deeper understanding of the industry’s financial landscape, this article will break down the key financial indicators that influence profitability and return on investment in the auto repair sector.
We will address the most pressing financial questions, including:
- What is the average annual revenue for an auto repair shop?
- What are the typical startup costs associated with opening an auto repair shop?
- How profitable are auto repair shops, and what profit margins can be expected?
Decoding Auto Repair Shop Revenue: How Much Do They Really Bring In?
Our analysis of approximately 2,800 auto repair businesses reveals that the average annual revenue stands at $1,226,000. However, it’s essential to recognize that this figure represents an average. The actual revenue of an individual auto repair shop can fluctuate significantly based on various factors. Location plays a pivotal role, with shops in densely populated or affluent areas often commanding higher revenue. The range of services offered also impacts earnings; shops specializing in niche repairs or offering comprehensive services may see different revenue streams compared to general repair shops. Finally, the scale of the business, from small independent garages to large franchise operations, naturally influences the overall revenue generated.
To provide a more granular view, let’s examine the median revenue across different auto repair franchises:
| Franchise | Number of Businesses | Median Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| Tire Pros | 623 | n.a. |
| Carstar | 430 | $2,265,000 |
| Fix Auto USA | 178 | $2,391,000 |
| Car-X | 145 | $778,000 |
| Merlin Complete Auto Care | 24 | $1,150,000 |
| Tuffy Tire and Auto Service | 163 | $1,344,000 |
| Abra Auto Body & Glass | 57 | n.a. |
| Honest-1 Auto Care | 64 | $1,149,000 |
| Maaco | 398 | $1,281,000 |
| Meineke Car Care Centers | 705 | $897,000 |
| Rad Air Complete Car Care | 10 | $1,102,000 |
| Weighted Average Revenue | 2,797 | $1,225,778 |

* n.a. – not available: some franchisors do not publicly disclose this information.
This table highlights the revenue variations among different franchises, reinforcing the point that “how much money do auto repair shops make” is not a one-size-fits-all answer. Factors like brand recognition, franchise support, and operational models all contribute to these differences.
Initial Investment: Understanding the Startup Costs for an Auto Repair Shop
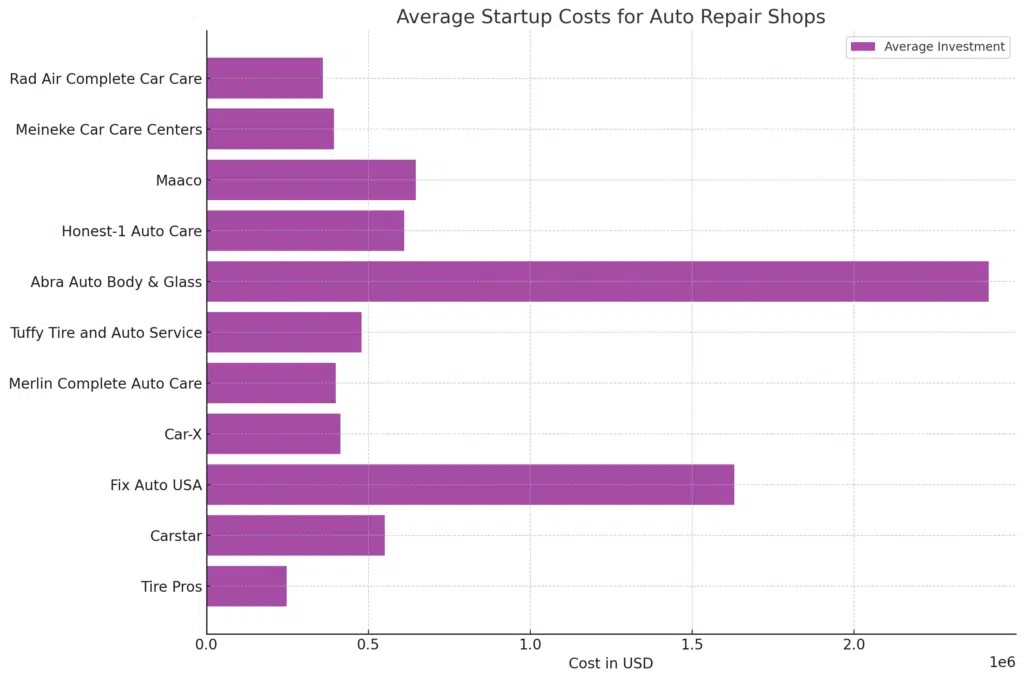
The initial investment required to launch an auto repair shop can be substantial and varies widely. Our data indicates that startup costs can range from $235,000 to $1,348,000. This broad range reflects the numerous variables involved in setting up such a business. The chosen location significantly impacts costs, with prime real estate demanding higher investment. The size and scope of the shop, from a small specialty repair service to a large multi-bay facility, also dictate the initial capital needed. Furthermore, the decision to start an independent shop or invest in a franchise carries different financial implications, with franchises often involving franchise fees and specific equipment requirements.
Let’s break down the investment ranges observed across different franchises:
| Franchise | Low Investment | High Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Tire Pros | $12,000 | $483,000 |
| Carstar | $298,000 | $804,000 |
| Fix Auto USA | $170,000 | $3,090,000 |
| Car-X | $315,000 | $512,000 |
| Merlin Complete Auto Care | $265,000 | $534,000 |
| Tuffy Tire and Auto Service | $229,000 | $729,000 |
| Abra Auto Body & Glass | $264,000 | $4,569,000 |
| Honest-1 Auto Care | $223,000 | $998,000 |
| Maaco | $276,000 | $1,016,000 |
| Meineke Car Care Centers | $227,000 | $562,000 |
| Rad Air Complete Car Care | $146,000 | $573,000 |
| Average Investment | $235,000 | $1,348,000 |
Startup Costs for a Medium-Sized Auto Repair Shop ($200,000 – $500,000)
For a more detailed understanding of where these startup funds are allocated, consider the typical costs associated with launching a medium-sized auto repair business. Budgeting between $200,000 and $500,000 can be a reasonable starting point. Here’s a breakdown of potential startup expenses:
- Equipment and Fixtures: Investing in essential equipment such as lifts, diagnostic tools, and repair fixtures. Range: $131,000 – $193,000
- Inventory: Establishing an initial stock of auto parts and supplies. Range: $5,000 – $24,000
- Leasehold Improvements: Modifying the leased space to meet the specific needs of an auto repair shop, including bay modifications and office build-out. Range: $8,000 – $64,000
- Training Expenses: Allocating funds for employee training prior to opening. Range: $3,000 – $5,000
- Pre-Opening Expenses: Covering initial setup costs like utility deposits and various setup fees. Range: $10,000 – $20,000
- Grand Opening Advertising: Launching marketing and advertising campaigns to announce the business opening. Range: $7,500
- Signage: Designing and installing prominent business signage for visibility. Range: $20,000 – $100,000
- Business Licenses and Permits: Securing the necessary legal operating permits and licenses. Range: $500
- Real Estate Costs: Initial lease payments for the shop premises. Range: $0 – $30,000
- Additional Funds (3 months): Maintaining sufficient working capital to cover operating expenses during the initial months. Range: $10,000 – $50,000
- Insurance (3 months): Securing essential insurance coverage for the first quarter of operation. Range: $4,000 – $5,000
Profitability in Auto Repair: What Kind of Margins Can You Expect?
Profitability is a key metric for assessing the financial success of any business. Auto repair shops, on average, report a 26% operating profit margin. This figure represents the profit generated from core operations, calculated after deducting operating expenses but before accounting for taxes and interest. Operating profit provides a clear picture of the efficiency and profitability of the shop’s day-to-day operations.
To further understand the profit dynamics, let’s examine key profitability metrics across different auto repair franchises:
Profitability Metrics for Auto Repair Franchises
| Franchise | COGS % | Gross Profit % | Labor Costs % | Operating Profit % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car-X | 35.2% | 64.8% | 30.3% | 19.9% |
| Merlin Complete Auto Care | 28.1% | 71.9% | 16.1% | 38.6% |
| Tuffy Tire and Auto Service | 30.8% | 69.2% | 28.2% | 26.3% |
| Meineke Car Care Centers | 26.3% | 73.7% | 19.2% | 24.2% |
| Rad Air Complete Car Care | 25.3% | 74.7% | 24.7% | 21.0% |
| Average | 29.14% | 70.86% | 23.7% | 26.0% |
This data reveals that while the average operating profit margin is 26%, individual franchises can experience variations. Factors such as cost management, service pricing strategies, and operational efficiency contribute to these differences in profitability.
Understanding Operational Costs: The Expenses of Running an Auto Repair Shop
To effectively manage and improve the financial performance of an auto repair shop, it’s crucial to understand the breakdown of operational costs. These expenses encompass everything from the direct costs of repairs to the overhead required to keep the business running smoothly. Here are the primary cost categories:
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): These are the direct expenses associated with providing repair services, primarily parts and materials. Typically, COGS can range from 25-35% of revenue.
- Labor Costs: This includes wages, benefits, and compensation for technicians and support staff. Labor costs are a significant expense, generally falling between 16-30% of revenue.
- Rent and Utilities: The costs associated with leasing or renting the shop premises and covering utilities such as electricity, water, and gas. These expenses typically account for 5-10% of revenue.
- Marketing and Advertising: Expenses dedicated to promoting the business and attracting customers, including online and offline marketing efforts. Allocate approximately 1-5% of revenue for marketing.
- Insurance: Premiums for various insurance coverages, including general liability, property insurance, and workers’ compensation. Insurance costs typically represent 2-4% of revenue.
- Supplies and Equipment Maintenance: Costs for maintaining and replacing tools and equipment, as well as purchasing consumable supplies used in repairs. Budget around 2-5% of revenue for these items.
- Administrative Expenses: General overhead costs such as office supplies, accounting services, and other administrative functions. These expenses typically fall within 5-10% of revenue.
- Training and Development: Investing in ongoing staff training to keep technicians updated with industry advancements and new technologies. Allocate approximately 1-3% of revenue for training.
- Miscellaneous Expenses: A category for other operational costs not included above, such as travel expenses, uniforms, and software subscriptions. These miscellaneous costs can be around 1-3% of revenue.
Profit-and-Loss Example: Maaco Auto Repair Shop
To illustrate these financial concepts in practice, let’s examine the profit-and-loss statement of Maaco auto repair shops. With 398 businesses analyzed in 2024, Maaco shops generated approximately $1,340,000 in yearly revenue and achieved an operating profit margin of 16.8%.
This example provides a real-world illustration of how revenue and expenses translate into profitability in an established auto repair franchise.
Auto Repair Financial Model Template: Plan for Success
For those seeking to delve deeper into the financial planning aspects of opening or managing an auto repair shop, resources like expert-built financial model templates can be invaluable. These tools, often available in Excel spreadsheet format, can assist in creating comprehensive 5-year financial projections for your business plan.
See the template
Buy
By understanding the revenue potential, startup costs, profitability margins, and operational expenses, aspiring and current auto repair shop owners can make informed decisions to optimize their business for financial success. The question of “how much money do auto repair shops make” is multifaceted, but with detailed data and careful planning, a thriving and profitable auto repair business is achievable.
