The automotive repair industry in the United States is a massive market, valued at $188.1 billion in 2024 and encompassing around 290,000 auto repair shops. If you’re considering entering this lucrative sector or simply curious about the financial performance of these businesses, a key question arises: how much does an auto repair shop make?
To answer this question with data-backed insights, we’ve analyzed the financial performance of over 3,300 auto repair businesses across the United States. This study, based on publicly available 2023 data, delves into the revenues, startup costs, and profitability of various auto repair franchises, including major players like Carstar, Fix Auto USA, and Meineke Car Care Centers.
Whether you are an aspiring entrepreneur exploring business opportunities or an industry enthusiast seeking financial benchmarks, this article provides a comprehensive overview of the earnings potential and financial dynamics within the auto repair industry. We will address crucial questions such as:
- What is the average revenue for an auto repair shop?
- What are the typical startup costs associated with opening an auto repair shop?
- How profitable are auto repair businesses on average?
Decoding Auto Repair Shop Revenue: What’s the Average Take?
Our analysis of approximately 2,800 auto repair businesses reveals that the average annual revenue for an auto repair shop is $1,226,000.
It’s important to note that this figure represents an average, and actual revenue can fluctuate significantly based on factors like location, the range of services offered, brand recognition, and the scale of operations. To provide a more granular view, let’s examine the median revenue across different franchise brands:
| Franchise | Number of Businesses | Median Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| Tire Pros | 623 | n.a. |
| Carstar | 430 | $2,265,000 |
| Fix Auto USA | 178 | $2,391,000 |
| Car-X | 145 | $778,000 |
| Merlin Complete Auto Care | 24 | $1,150,000 |
| Tuffy Tire and Auto Service | 163 | $1,344,000 |
| Abra Auto Body & Glass | 57 | n.a. |
| Honest-1 Auto Care | 64 | $1,149,000 |
| Maaco | 398 | $1,281,000 |
| Meineke Car Care Centers | 705 | $897,000 |
| Rad Air Complete Car Care | 10 | $1,102,000 |
| Weighted Average Revenue | 2,797 | $1,225,778 |

* n.a. – not available: Some franchisors do not publicly disclose this information.
As the table indicates, revenue can vary widely depending on the franchise. Brands like Fix Auto USA and Carstar report higher median revenues, while others like Car-X and Meineke Car Care Centers show lower figures. This variation underscores the impact of brand strength, service specialization, and operational strategies on a shop’s earning potential.
Navigating Startup Costs: Investing in Your Auto Repair Venture
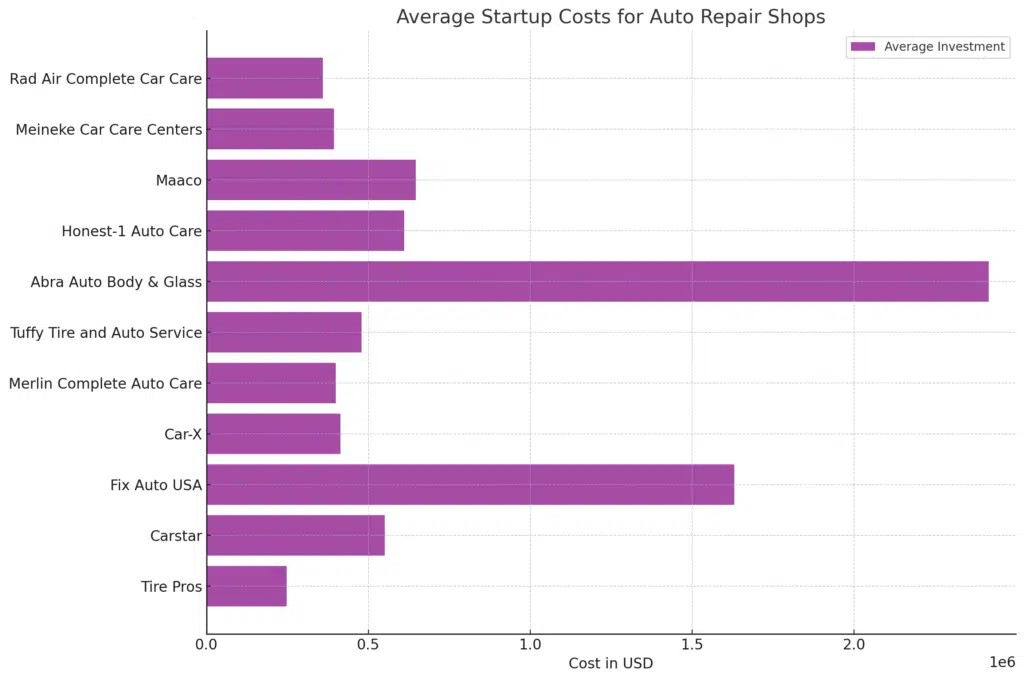
The initial investment required to launch an auto repair shop can be substantial and varies considerably. Our data indicates that startup costs can range from $235,000 to $1,348,000 on average. This wide range reflects the numerous factors influencing initial expenses, such as location, facility size, equipment choices, and franchise fees (if applicable).
Let’s break down the investment ranges across different franchises to provide a clearer picture:
| Franchise | Low Investment | High Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Tire Pros | $12,000 | $483,000 |
| Carstar | $298,000 | $804,000 |
| Fix Auto USA | $170,000 | $3,090,000 |
| Car-X | $315,000 | $512,000 |
| Merlin Complete Auto Care | $265,000 | $534,000 |
| Tuffy Tire and Auto Service | $229,000 | $729,000 |
| Abra Auto Body & Glass | $264,000 | $4,569,000 |
| Honest-1 Auto Care | $223,000 | $998,000 |
| Maaco | $276,000 | $1,016,000 |
| Meineke Car Care Centers | $227,000 | $562,000 |
| Rad Air Complete Car Care | $146,000 | $573,000 |
| Average Investment | $235,000 | $1,348,000 |
For a more detailed understanding of typical startup expenses, consider the cost breakdown for a medium-sized auto repair shop, which generally falls within the $200,000 to $500,000 investment range:
Typical Startup Costs for a Medium-Sized Auto Repair Shop
When budgeting for your auto repair business, consider these key startup cost categories:
- Equipment and Fixtures: Investing in essential equipment like lifts, diagnostic tools, and other fixtures is a major upfront cost. Expect to allocate $131,000 – $193,000 for this category.
- Inventory: Building an initial inventory of parts and supplies is crucial for smooth operations. Budget around $5,000 – $24,000 for your starting inventory.
- Leasehold Improvements: Modifying a leased space to meet the specific needs of an auto repair shop, including bay construction and office setup, can cost $8,000 – $64,000.
- Training Expenses: Investing in pre-opening training for your staff ensures service quality and efficiency from day one. Allocate $3,000 – $5,000 for training.
- Pre-Opening Expenses: Various miscellaneous costs incurred before opening, such as utility deposits and permits, can add up to $10,000 – $20,000.
- Grand Opening Advertising: Generating initial buzz and attracting customers requires a dedicated marketing budget for your grand opening. Plan for approximately $7,500 for launch advertising.
- Signage: Visible and professional signage is vital for attracting walk-in customers. Signage costs can range from $20,000 – $100,000 depending on complexity and location.
- Business Licenses and Permits: Securing the necessary licenses and permits is a mandatory step, with fees typically around $500.
- Real Estate Costs: Initial rent or lease payments can vary significantly depending on location and property size, ranging from $0 – $30,000.
- Additional Funds (3 months): Maintaining sufficient working capital to cover operational expenses during the initial months is crucial for business survival. Set aside $10,000 – $50,000 for the first three months of operation.
- Insurance (3 months): Protecting your business with adequate insurance coverage from the outset is essential. Budget $4,000 – $5,000 for the first three months of insurance premiums.
Profitability Insights: How Much Can Auto Repair Shops Really Earn?
Despite the significant startup costs, the auto repair industry can be quite profitable. On average, auto repair shops report a 26% operating profit margin. This margin represents the profit generated from core operations, before accounting for taxes and interest expenses. It’s a key indicator of the underlying profitability of the business model.
To further illustrate profitability, let’s examine key financial metrics across various auto repair franchises:
Key Profitability Metrics for Auto Repair Franchises
| Franchise | COGS % | Gross Profit % | Labor Costs % | Operating Profit % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car-X | 35.2% | 64.8% | 30.3% | 19.9% |
| Merlin Complete Auto Care | 28.1% | 71.9% | 16.1% | 38.6% |
| Tuffy Tire and Auto Service | 30.8% | 69.2% | 28.2% | 26.3% |
| Meineke Car Care Centers | 26.3% | 73.7% | 19.2% | 24.2% |
| Rad Air Complete Car Care | 25.3% | 74.7% | 24.7% | 21.0% |
| Average | 29.14% | 70.86% | 23.7% | 26.0% |
As shown in the table, gross profit margins are generally high in the auto repair industry, averaging around 70.86%. However, operating profit margins vary, with some franchises like Merlin Complete Auto Care achieving significantly higher profitability compared to others like Car-X. Efficient cost management, particularly in labor and COGS, plays a crucial role in maximizing profitability.
Understanding the Costs of Running an Auto Repair Shop
To maintain a profitable auto repair shop, it’s essential to manage ongoing operational costs effectively. These costs typically include:
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): This encompasses the direct costs of parts and materials used in repair services. COGS typically range from 25-35% of revenue.
- Labor Costs: Wages, salaries, and benefits for technicians and service staff constitute a significant expense, usually around 16-30% of revenue.
- Rent and Utilities: Facility costs, including rent, electricity, water, and gas, typically represent 5-10% of revenue.
- Marketing and Advertising: Ongoing marketing efforts to attract and retain customers generally consume 1-5% of revenue.
- Insurance: Maintaining adequate insurance coverage, including liability and workers’ compensation, accounts for approximately 2-4% of revenue.
- Supplies and Equipment Maintenance: Regular maintenance and replacement of tools and equipment, along with consumable supplies, require 2-5% of revenue.
- Administrative Expenses: General overhead costs like office supplies, accounting, and administrative staff salaries typically amount to 5-10% of revenue.
- Training and Development: Investing in continuous staff training to keep up with automotive technology advancements usually costs 1-3% of revenue.
- Miscellaneous Expenses: Other operational costs, such as travel, uniforms, and software subscriptions, make up 1-3% of revenue.
Real-World Example: Maaco Auto Repair Profit & Loss
Examining a real-world example can further clarify the financial dynamics of an auto repair shop. Maaco, with 398 locations in 2024, provides a representative case. With an average yearly revenue of $1,340,000, Maaco shops achieve an operating profit margin of 16.8% per month.
{{product_image|medium}}
This example highlights the potential for substantial revenue and healthy profit margins in the auto repair industry, even with considerable operating expenses.
Leverage Financial Modeling for Success
For a more in-depth financial understanding and to aid in business planning, consider utilizing specialized tools like an auto repair financial model template. These Excel spreadsheets, designed by experts, offer 5-year projections and allow for scenario planning to optimize your business strategy.
See the template
Buy
By understanding the revenue potential, startup costs, profitability drivers, and operational expenses of auto repair shops, aspiring entrepreneurs and industry participants can make informed decisions and navigate the path to success in this robust market.
