Dealing with car repairs after a collision can be disruptive. Finding alternative transportation while your vehicle is in the shop adds stress to an already inconvenient situation. Understandably, one of the first questions on any car owner’s mind after an accident is: “How long does it take to repair my car?”
At Car Repair Online, we understand the importance of clear expectations. With years of experience in the auto repair industry, we’ve created this comprehensive guide to break down car repair timelines. We aim to provide you with a realistic understanding of the repair process, typical durations for different types of damage, and the factors that can influence the overall repair time. Knowing what to expect can significantly reduce stress and help you navigate the repair process more smoothly.
Decoding Average Car Repair Times
The question “how long does it take to repair car” doesn’t have a single, straightforward answer. Repair duration is highly variable, influenced primarily by the extent of the damage and a range of other contributing factors. Generally, car repairs can take anywhere from just a few hours to several weeks, or even longer in complex cases.
Alt text: Chart illustrating average car repair times for different types of collision damage, ranging from minor to major repairs.
To give you a clearer picture of typical car repair durations, we’ve compiled a table outlining average repair times based on the severity and type of damage:
| Type of Collision Repair | Average Time to Fix |
|---|---|
| Minor Collision Repair | 1-3 days |
| Major Collision Repair | 1 to 3 weeks |
| Paintless Dent Repair | 1-2 days |
| Bumper Repair/Replacement | 1-3 days |
| Fender Repair/Replacement | 1-4 days |
| Door Repair/Replacement | 2-4 days |
| Glass Replacement | 1-2 days |
| Suspension Repair | 2-3 days |
| Frame Straightening | 4 days – 2 weeks |
| Paint Repair (minor) | 2-4 days |
| Paint Repair (major) | 1-2 weeks |
| Airbag Replacement | 2-5 days |
| Engine Repair/Replacement | 1-4 weeks |
| Full Vehicle Restoration | 4-8 weeks or longer |











Minor vs. Major Car Repair: Understanding the Time Differences
Car repairs generally fall into two broad categories: minor and major. Understanding the distinction between these categories is key to estimating how long your car repair might take.
Minor Car Repair Time
Minor car repairs are typically completed within 1 to 3 days. These repairs address superficial damage that doesn’t impact the vehicle’s structural integrity or major systems. They often involve cosmetic fixes and are less labor-intensive.
Examples of minor car repairs include:
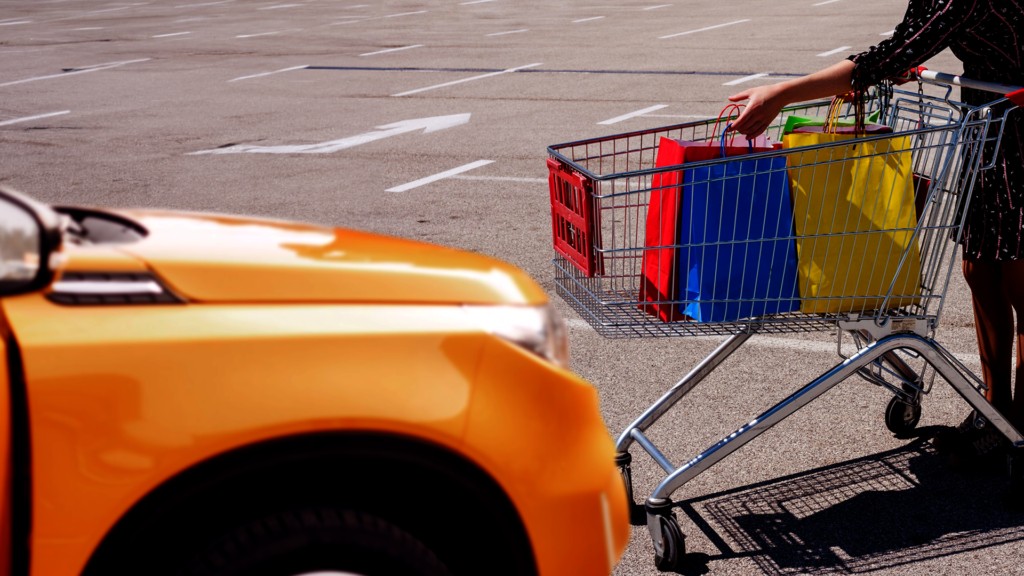
- Shopping Cart Dents: Small dents caused by runaway shopping carts or minor impacts.
Alt text: Image of a car door with a small dent, typical of damage from a shopping cart collision.
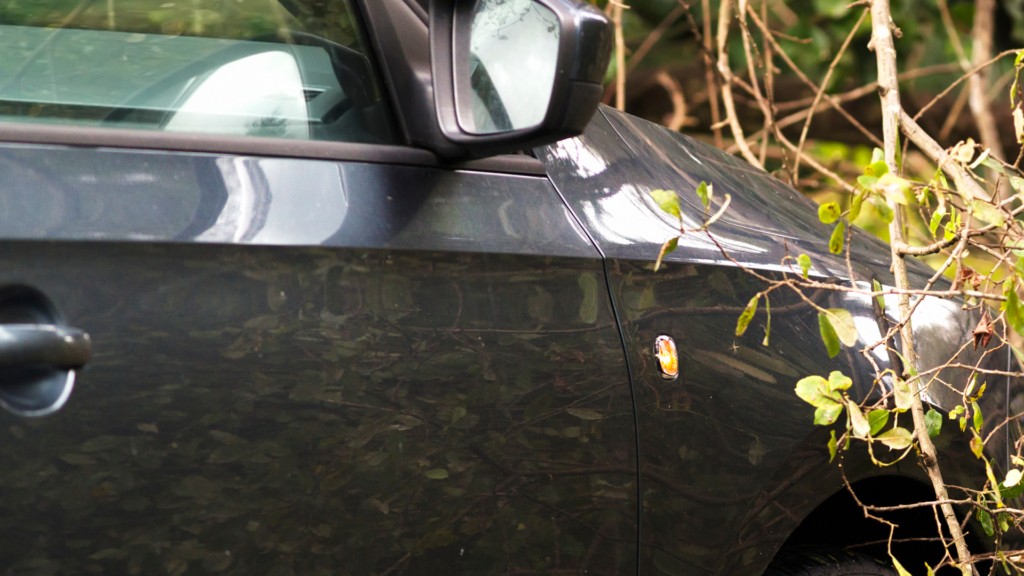
- Tree Branch Scratches: Surface scratches to the paintwork caused by tree branches or bushes.
Alt text: Close-up photo showing shallow scratches on a car’s paint, resulting from contact with a tree branch.
- Minor Road Debris Damage: Small paint chips and scratches from stones or road debris.
Alt text: Image highlighting minor paint damage, such as small chips and scratches, commonly caused by road debris.
Major Car Repair Time
Major car repairs typically extend from 1 to 3 weeks and address more significant damage. These repairs involve structural issues, mechanical problems, or replacement of safety-critical components. They require specialized equipment, skilled technicians, and potentially longer wait times for parts.
Examples of major car repairs include:
- Rear-End Collisions: Damage to the rear of the vehicle, potentially affecting the trunk, bumper, and frame.
Alt text: Photo of a car with significant rear-end damage, including a crumpled trunk and bumper after a collision.
- Side-Impact (T-Bone) Collisions: Damage to the side of the vehicle, impacting doors, side panels, and potentially the vehicle frame.
Alt text: Image of a car showing substantial side-impact damage, with a crushed door and damaged side panel from a T-bone accident.
- Parking Lot Collisions with Structures: Damage from hitting poles, barriers, or other stationary objects, often affecting bumpers, fenders, and front-end components.
Alt text: Picture of a car with front-end damage, including a damaged bumper and bent fender, from an impact with a pole or barrier in a parking lot.
Severe Collision Damage: Extended Repair Times
In cases of severe collision damage, car repair times can exceed 3 weeks. This category includes extensive frame damage, situations requiring hard-to-find parts, or complex mechanical repairs. The more extensive the damage, the longer it will take to restore your vehicle to its pre-accident condition.
Examples of severe collision damage scenarios:
- High-Speed Head-On Collisions: Extensive front-end damage, potentially involving engine damage, frame damage, and significant bodywork.
Alt text: Image depicting a car with severe front-end damage from a high-speed collision, showing a crushed front end, crumpled hood, and broken windshield.
- Rollover Accidents: Damage to multiple areas of the vehicle, including the roof, sides, undercarriage, and potentially requiring extensive structural repair.
Alt text: Photo of a car that has rolled over, illustrating damage to the roof, sides, and undercarriage from the accident.
- Severe High-Speed Side-Impact Collisions: Extensive damage to the side of the vehicle, potentially compromising the frame and requiring significant structural repairs.
Alt text: Picture of a car with severe side-impact damage from a high-speed collision, including a crushed door, damaged side panel, and potential frame damage.
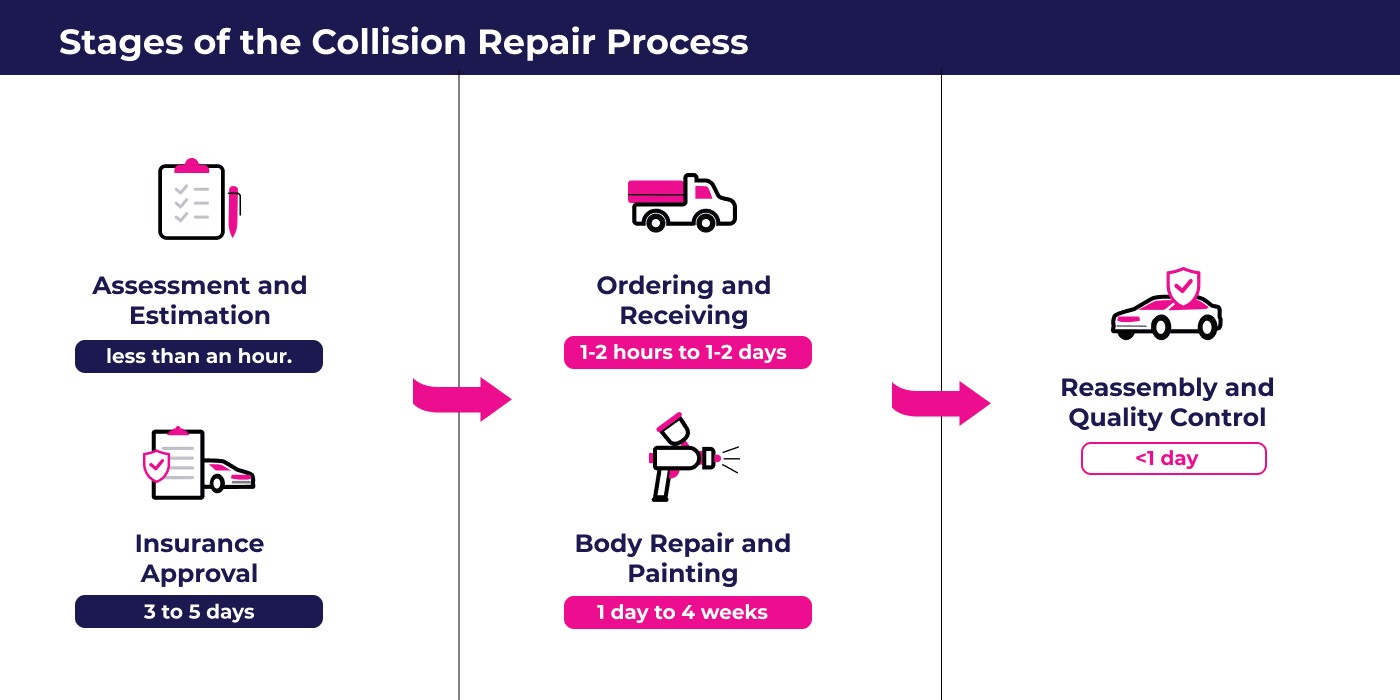
Understanding the Stages of the Car Repair Process
To better understand the timeline for your car repair, it’s helpful to know the typical stages involved in the process. Each stage contributes to the overall repair duration.
Alt text: Flowchart outlining the stages of the car collision repair process, from initial assessment to final quality control.
1. Initial Assessment and Estimate
The first step in any car repair is a thorough assessment of the damage. A qualified technician will inspect your vehicle to determine the extent of the damage, identify necessary repairs, and prepare a detailed estimate. This estimate will outline the cost of parts and labor, and provide an initial timeframe for the repair.
Typical Timeframe: Generating a comprehensive estimate can take anywhere from a few hours to a full day, depending on the complexity of the damage and the shop’s workload. Some shops, like those focused on efficient customer service, may offer quicker estimate times.
2. Insurance Approval (If Applicable)
If you are filing an insurance claim for the repairs, the estimate will need to be submitted to your insurance company for review and approval. The insurance adjuster will assess the estimate to ensure the repairs are necessary and the costs are reasonable based on your policy and the damage. Negotiation between the repair shop and the insurance company may occur during this stage.
Typical Timeframe: Insurance approval can take 3 to 5 business days, or potentially longer if there are complexities or disagreements regarding the repair plan.
3. Parts Ordering and Procurement
Once the estimate is approved, and the necessary repairs are determined, the repair shop will order the required replacement parts. The time it takes to obtain parts depends on factors like part availability, vehicle make and model, and whether original equipment manufacturer (OEM) or aftermarket parts are used.
Typical Timeframe: Parts procurement can range from a few hours to several days. Common parts for popular vehicles are usually readily available, while specialized or rare parts may take longer to source, potentially extending the overall repair time.
4. Body Repair and Painting
This is the core repair phase where technicians perform the necessary bodywork, including dent removal, panel replacement, frame straightening, and other structural repairs. Once the bodywork is complete, the vehicle will move to the painting stage. This involves matching the original paint color, applying primer, base coat, and clear coat, and ensuring a seamless finish.
Typical Timeframe: Body repair and painting can take 1 day to 4 weeks, depending heavily on the severity of the damage. Minor cosmetic repairs will be significantly faster than major structural repairs and multi-panel paintwork.
5. Reassembly and Quality Control
After painting, the vehicle is reassembled, with detail pieces, moldings, and trim being reinstalled. Following reassembly, a thorough quality control inspection is performed. This includes checking the aesthetics of the repair, ensuring proper functionality of all systems, and verifying the vehicle’s safety and performance.
Typical Timeframe: Reassembly and quality control typically take a few hours to a full day to ensure everything is correctly fitted and functioning as expected.
6. Potential for Additional Delays: Hidden Damage and Unexpected Issues
It’s important to be aware that unforeseen issues can arise during the repair process, potentially extending the timeline. Hidden damage, discovered only after disassembly, or the need for additional specialized repairs (like frame straightening or wheel alignment) can add time to the repair. Supply chain disruptions and high workloads at the repair shop can also contribute to delays.
Key Factors Influencing Car Repair Duration
Several factors directly impact how long it takes to repair a car. Understanding these factors can help you anticipate potential delays and have more realistic expectations.
Alt text: Graphic illustrating key factors that influence the duration of car collision repairs, including damage severity and parts availability.
1. Severity of Damage: Minor vs. Major Impacts
As previously discussed, the severity of the damage is the most significant determinant of repair time. Minor damage, like scratches or dents, will naturally result in a faster repair time compared to major structural damage requiring extensive bodywork and part replacements. The cost of repair also correlates with damage severity, ranging from a few hundred dollars for minor fixes to tens of thousands for major collision repairs.
2. Parts Availability: OEM vs. Aftermarket and Supply Chains
The availability of replacement parts is a critical factor. Common parts for popular vehicle models are usually readily available, minimizing delays. However, if your vehicle requires rare, specialized, or OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts, sourcing these can take longer. Supply chain disruptions, which have become more common globally, can also impact parts availability and lead to extended repair times. Aftermarket parts might be more readily available but could have variations in quality compared to OEM parts, potentially affecting long-term durability.
3. Vehicle Type: Common vs. Luxury/Rare Models
The type of vehicle you drive plays a role in repair time. Repairs for common vehicles from brands like Toyota, Honda, Ford, and Chevrolet are often quicker and more affordable due to readily available parts and experienced technicians. Luxury or rare vehicles, such as Mercedes-Benz, BMW, Audi, Lexus, and Tesla, often require specialized parts, tools, and technicians trained in handling their unique features and technologies. Repairs for these vehicles can take longer and be more expensive, particularly if rare parts are needed or if the vehicle has advanced technology systems requiring specific expertise.
4. Insurance Company Involvement: Claims Processing Time
Involving your insurance company in the repair process adds another layer of administration and potential time. Filing claims, waiting for adjuster assessments, and obtaining approvals can extend the overall repair timeline. While insurance coverage is beneficial for managing repair costs, it’s important to factor in the additional time for claim processing. Choosing a repair shop that has experience working with insurance companies can help streamline this process.
5. Repair Shop Workload: Shop Capacity and Scheduling
The workload of the chosen auto repair shop can also influence repair time. Busy shops may have longer lead times for scheduling repairs and potentially longer turnaround times due to the volume of vehicles they are servicing. Choosing a reputable and well-organized shop is important. While a busy shop might indicate quality service, it’s worth inquiring about their current workload and estimated repair timelines upfront.
Conclusion: Patience and Communication are Key
While it’s natural to wonder “how long does it take to repair car” after an accident, remember that the answer is variable and depends on numerous factors. Repair times can range from a single day for minor fixes to several weeks for major collision repairs.
Understanding the stages of the repair process and the factors that influence the timeline can help you manage your expectations and navigate the repair process with less stress. Patience is essential, especially in cases of significant damage or when dealing with insurance claims and parts procurement.
Choosing a reputable auto repair service is crucial. A good shop will maintain clear communication with you throughout the process, provide regular updates on the repair progress, and strive to complete the repairs efficiently without compromising quality. Open communication and realistic expectations are key to a smoother and less stressful car repair experience.
Average Car Repair Time FAQs
What are my transportation options while my car is being repaired?
Finding transportation while your car is in the shop is a common concern. Depending on your insurance policy, you may have rental car coverage. Check your policy details to see if rental car reimbursement is included. Some auto repair shops also offer courtesy vehicles or shuttle services to assist customers with transportation needs. Inquire with your chosen repair shop about their transportation assistance options.
Do auto repair shops offer warranties on their work?
Reputable auto repair shops typically offer warranties on their repair work. Warranties can vary in duration and coverage, so it’s important to ask about the specific warranty offered by the shop you choose. A warranty provides peace of mind and assures you of the quality of the repairs performed.
Is front-end or rear-end collision repair typically faster?
Generally, rear-end collision repairs are often faster and less expensive than front-end repairs. The front of a vehicle houses more complex systems, including the engine, radiator, and various components, making front-end repairs potentially more intricate and time-consuming. Rear-end damage may often be more localized and less likely to impact critical vehicle systems.
When is a car considered a total loss by insurance?
An insurance company typically declares a car a “total loss” when the cost of repairing the vehicle exceeds its actual cash value (ACV) or reaches a certain threshold, often around 70-75% of the ACV. In such cases, the insurance company may deem it more economical to declare the vehicle a total loss and compensate the owner for the car’s pre-accident value, rather than paying for extensive repairs.
What should I do if my car repair is taking longer than initially estimated?
If your car repair is significantly exceeding the initial estimate, the first step is to communicate directly with the auto repair shop. Inquire about the reasons for the delay. There might be unforeseen issues, parts delays, or complexities that have arisen. Open communication can help clarify the situation. If you are concerned or unsatisfied with the explanation, you can contact your insurance company to discuss the situation and explore your options.
How much should I expect to pay for car collision repair?
The cost of car collision repair is highly variable and depends on the extent of the damage, the type of vehicle, parts costs, and labor rates. Minor repairs might cost a few hundred dollars, while major collision repairs can range from several thousand to tens of thousands of dollars. Obtaining a detailed and transparent estimate from a reputable repair shop is essential to understand the expected costs for your specific repair needs.
