When your car starts showing signs of electrical trouble, like headlights dimming unexpectedly or the engine struggling to turn over due to a weak battery, a faulty alternator often comes to mind as a potential culprit. Before rushing to the mechanic, you might wonder if a car diagnostic tool, such as an OBD2 scanner, can help you pinpoint whether a bad alternator is indeed the problem.
The short answer is yes, a car diagnostic tool can be instrumental in detecting a bad alternator, although it’s not always a direct diagnosis.
Let’s delve into how an OBD2 scanner, like the Foxwell NT1009, can be used as a valuable tool in assessing your alternator’s health. We’ll explore the steps involved in using these devices to identify potential alternator issues, empowering you to understand if your alternator needs attention or if the electrical gremlins lie elsewhere.
Understanding the Vital Role of the Alternator
The alternator is a critical component within your vehicle’s electrical system. Think of it as the heart of your car’s electrical lifeblood. Its primary function is to generate electricity while the engine is running. This electricity powers all of your car’s electrical components, from the headlights and infotainment system to vital engine management systems. Crucially, the alternator also recharges your car battery, ensuring it has enough power to start the engine the next time you turn the key.
Alternators, like all mechanical components, have a lifespan. Over time, they can wear out or fail. Common symptoms indicating a potential alternator problem include:
- Dimming Headlights: If your headlights appear weaker than usual, especially at idle, it could signal the alternator isn’t producing enough power.
- Slow Engine Start-up or Clicking Noises: A weak or failing alternator might not be adequately charging the battery, leading to slow engine cranking or a clicking sound when you try to start the car.
- Dead Battery: While batteries can fail on their own, a consistently dead battery, especially a relatively new one, could point to an alternator that isn’t recharging it properly.
- Warning Lights: The battery warning light or “ALT” (alternator) light on your dashboard might illuminate, indicating a problem within the charging system.
- Electrical System Issues: Problems with other electrical components, such as power windows operating slowly or the radio cutting out, can also be symptoms of alternator trouble.
Recognizing these early warning signs can save you from being stranded and potentially prevent more costly repairs down the road.
How Car Diagnostic Tools Aid in Alternator Issue Detection
A car diagnostic tool, specifically an OBD2 scanner like the Foxwell NT1009, is an invaluable asset when investigating potential alternator problems. These tools work by communicating with your car’s computer system, reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that are stored when the system detects an anomaly.
It’s important to understand that an OBD2 scanner might not directly declare “bad alternator.” Instead, it excels at identifying related electrical system issues that can strongly suggest alternator failure. For example, codes indicating “low voltage” (like P0562) or malfunctions in the “alternator field control circuit” (such as P0622) are significant clues that point towards alternator problems. These codes, along with live data readings, help you narrow down the possibilities and determine if the alternator is the likely source of the electrical issues.
Step-by-Step Guide: Using an OBD2 Scanner to Check for Alternator Issues
Here’s how to use an OBD2 scanner, like the Foxwell NT1009, to investigate potential alternator problems:
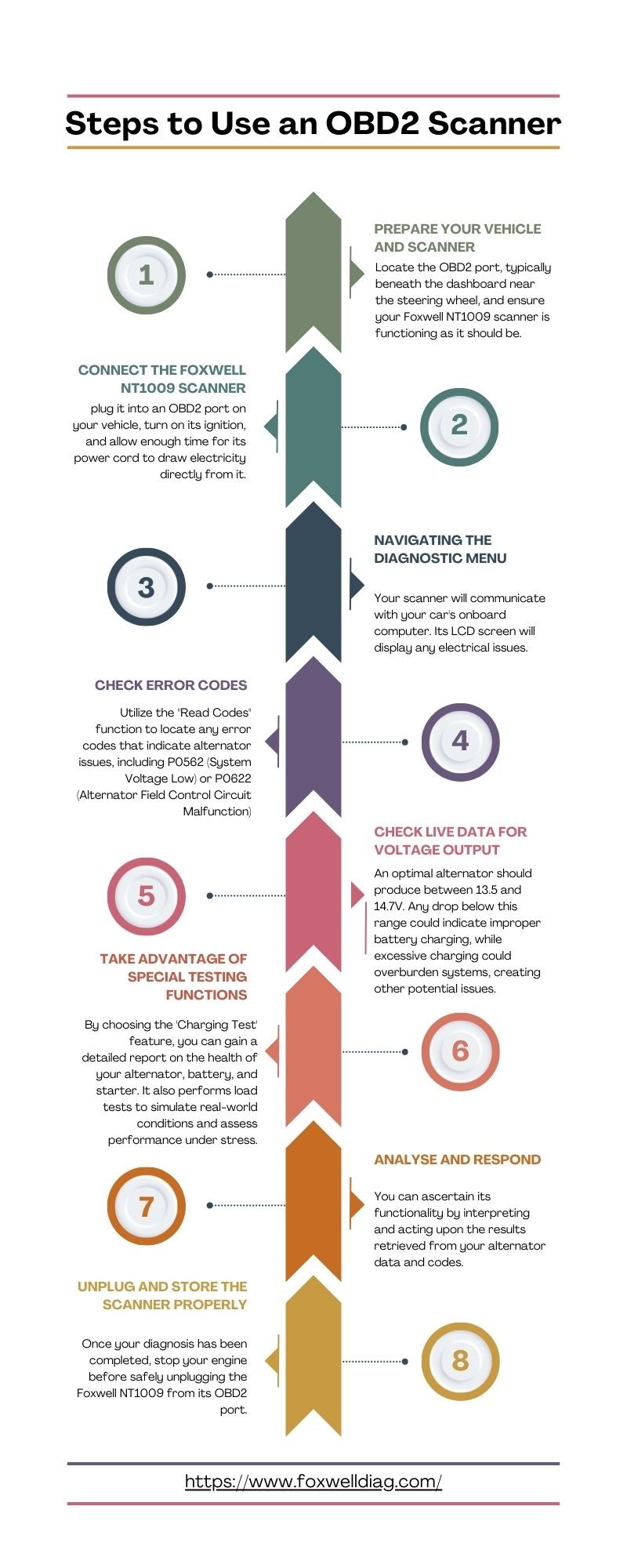
1. Preparation: Vehicle and Scanner Readiness
Begin by ensuring your vehicle is properly prepared. Turn off all unnecessary electrical loads, such as headlights, radio, and air conditioning. This minimizes electrical draw during the test. Locate your car’s OBD2 port. It’s typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side, near the steering column. Confirm that your Foxwell NT1009 scanner is powered on and functioning correctly.
2. Connecting the Foxwell NT1009 Scanner
Plug the Foxwell NT1009 scanner securely into the OBD2 port. Turn your car’s ignition to the “ON” position, but do not start the engine yet. This allows the scanner to draw power and establish communication with your vehicle’s computer system. Give the scanner a moment to initialize and connect before proceeding.
3. Navigating to the Diagnostic Menu
On your Foxwell NT1009 scanner, navigate through the menu options to find the “Diagnostic” or “OBD2/EOBD” section. Select this option. You may be prompted to enter your vehicle’s make, model, and year for more accurate diagnostics. Follow the on-screen prompts to input this information.
4. Reading Error Codes for Clues
Use the “Read Codes” or “Trouble Codes” function on the scanner. The scanner will display any stored diagnostic trouble codes. Look for codes that are relevant to the charging system or voltage issues. Codes like P0562 (System Voltage Low), P0622 (Alternator Field Control Circuit Malfunction), or other voltage-related codes are potential indicators of an alternator problem. Note down any codes present.
5. Examining Live Data for Voltage Output
One of the most valuable features for alternator testing is the “Live Data” or “Data Stream” function. Access this feature on your Foxwell NT1009. Start your car’s engine. Within the live data stream, look for parameters related to voltage, specifically “Battery Voltage” or “System Voltage.”
A healthy alternator should typically produce a voltage reading between 13.5 and 14.7 volts when the engine is running. Readings consistently below this range suggest the alternator might not be charging adequately. Conversely, excessively high voltage can also indicate alternator regulation issues.
To further assess alternator performance, turn on electrical accessories like headlights, air conditioning, and the radio to increase the electrical load. Observe if the voltage reading drops significantly under load. A substantial voltage drop can indicate a failing alternator struggling to keep up with demand.
6. Utilizing Special Charging System Tests
The Foxwell NT1009, and some other advanced scanners, offer specialized “Charging System Tests” or “Alternator Tests.” Explore your scanner’s menu for such options. These tests often perform a more comprehensive evaluation of the charging system, including the alternator, battery, and starter. They may conduct load tests to simulate real-world driving conditions and assess the alternator’s performance under stress. Follow the scanner’s prompts to run these specialized tests and review the detailed reports they generate.
7. Analyzing Results and Determining Next Steps
Carefully analyze the results from error codes, live voltage data, and any specialized tests you performed.
- Normal Readings: If voltage readings are within the 13.5-14.7V range, and no relevant error codes are present, your alternator might be functioning correctly. However, if symptoms persist, further investigation is still recommended.
- Low Voltage or Relevant Error Codes: Consistently low voltage readings, especially under load, or the presence of codes like P0562 or P0622 strongly suggest a potential alternator problem.
- High Voltage: Readings significantly above 14.7V might indicate an overcharging alternator, which can also damage the battery and other electrical components.
Based on your findings, you can decide on the next course of action. This might involve further testing, consulting a mechanic, or considering alternator replacement.
8. Disconnecting and Storing the Scanner
Once you have completed your diagnosis, turn off your car’s engine. Safely disconnect the Foxwell NT1009 scanner from the OBD2 port. Store your scanner in a clean, dry place, ready for future use. You can use the scanner to clear any diagnostic trouble codes after completing repairs, if necessary.
Alternative Methods to Evaluate Your Alternator
Even with a car diagnostic tool, it’s beneficial to be aware of alternative methods for alternator testing. These methods can provide additional confirmation or be used if you don’t have access to a scanner.
A multimeter is a simple and effective tool for basic alternator voltage testing. With the engine running, connect the multimeter probes to the battery terminals. A reading between 13.5V and 14.7V generally indicates a functioning alternator.
A load test provides a more rigorous assessment of alternator performance under demanding electrical loads. This test can be performed using specialized load testing equipment or by a professional mechanic. It measures the alternator’s ability to maintain voltage output when subjected to increased electrical demand, offering a more comprehensive evaluation of its health.
Conclusion: OBD2 Scanners as a Key Diagnostic Aid
In conclusion, a car diagnostic tool like the Foxwell NT1009 is a powerful first step in determining if a bad alternator is causing your car’s electrical problems. While it may not provide a definitive “bad alternator” diagnosis directly, it offers invaluable insights through error codes, live voltage monitoring, and specialized tests.
OBD2 scanners are excellent for early problem detection and providing data to guide your next steps. However, remember that they are part of a diagnostic process. In some cases, especially with intermittent issues or complex electrical problems, supplementary testing with a multimeter or a professional load test might be necessary to confirm alternator failure.
By regularly using a car diagnostic tool and understanding its capabilities in conjunction with other testing methods, you can proactively maintain your vehicle’s electrical system, minimize the risk of unexpected breakdowns, and potentially save on costly repairs.
FAQs About Car Diagnostic Tools and Alternators
Can you test an alternator with an OBD2 scanner?
Yes, an OBD2 scanner is a helpful tool for testing an alternator. It can read trouble codes related to charging system issues and monitor live voltage data, providing valuable clues about alternator performance. However, it might not always give a direct “bad alternator” diagnosis, and further testing may be needed.
Will a bad alternator show up on a scan?
A bad alternator can trigger related trouble codes that will show up on a scan. These codes might indicate low system voltage, problems in the alternator control circuit, or other electrical anomalies that point to a potential alternator issue. While the scan might not say “bad alternator” explicitly, it will provide strong indicators for further investigation.
Is there an OBD code specifically for alternator failure?
While there isn’t one single OBD code that says “alternator failed,” there are codes strongly associated with alternator problems. Common codes like P0562 (System Voltage Low) and P0622 (Alternator Field Control Circuit Malfunction) are frequently triggered by alternator issues and are critical indicators to consider during diagnosis.